| Frankfurt Quasar Monitoring |
| MRK 478 |
| Cross-Identifications | PG
1440+356, IRAS 14400+3539, PGC 52510 2MASSi J1442074+352622, EUVE J1442+35.4 FIRST J144207.4+352623, RX J1442.1+3526 1AXG J144207+3526, 2XMM J144207.4+352622 GALEXASC J144207.57+352623.7, 1440+356 SDSS J144207.47+352622.9, 1H 1429+370 Markarian 478 |
| Equat. coordinates | RA 14 42 07.5 DE +35 26 23 (J2000) |
| Constellation | Bootes |
| Type | QSO |
| Redshift (2) |
z=0.079 |
|
Distance
(2)
(3)
|
321 Mpc |
| Total mag range (mv) (4) | 14.3 - 14.8 |
| Catalog Magnitude (1) | 14.58 |
| Absolute Magnitude (1) | -23.4 MB |
| Light Travel-Time (2) | 1.009 × 109 yrs |

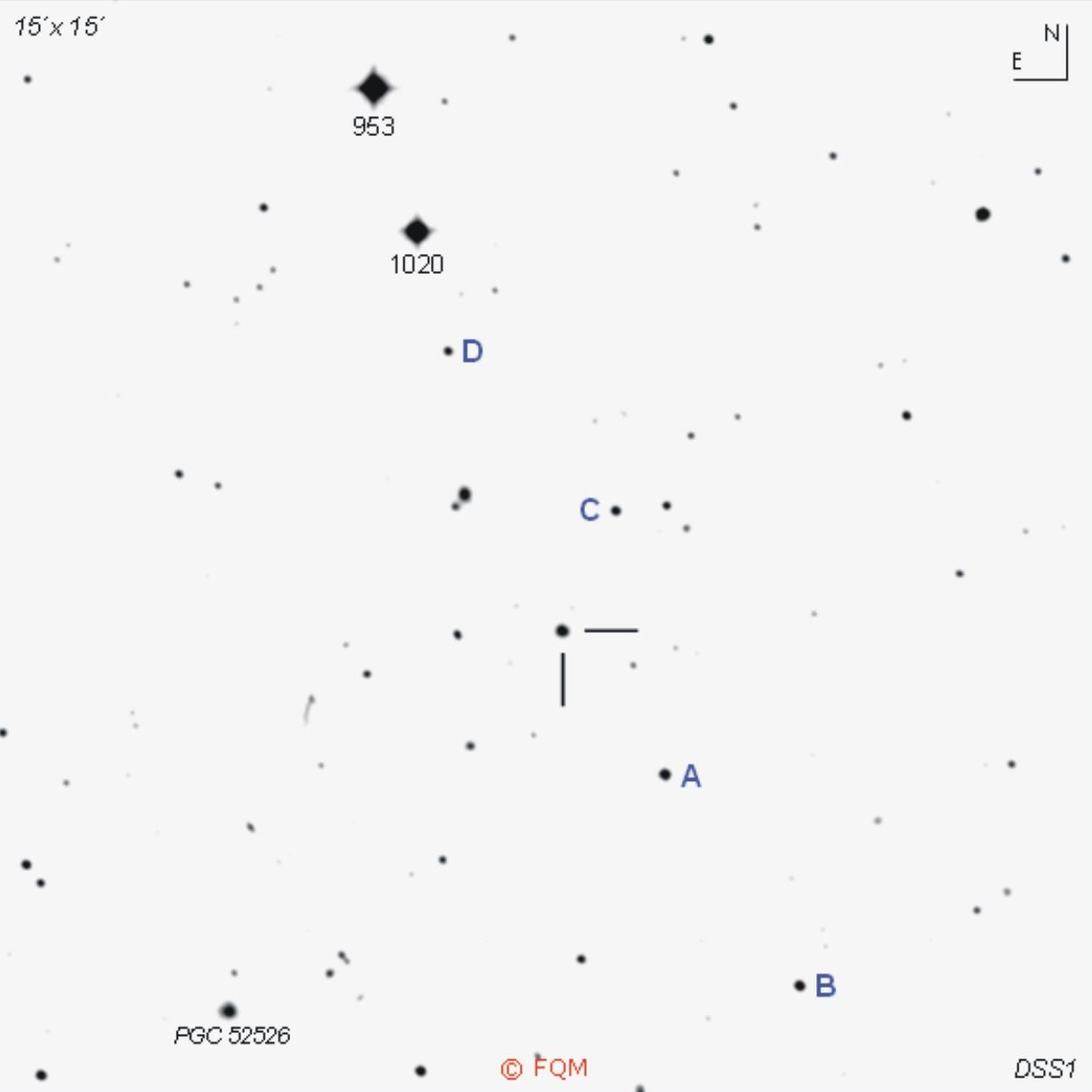
Comparison stars
| star | B | V |
| A | 14.457 (0.063) |
13.840 (0.061) |
| B | 14.846 (0.073) |
14.139 (0.066) |
| C | 15.252 (0.048) |
14.612 (0.066) |
| D | 15.736 (0.193) | 15.159 (0.118) |



| Markarian 478
(MRK
478 for short)
is a bright quasar in Bootes, about 3.5° SE of Gamma Bootis. MRK
478 was discovered in 1972 by the UV-Continuum-Survey run by
Markarian et al. (MRK) at the Astrophysical Observatory in
Byurakan/Armenia.
Main goal was the
spectroscopic search for "blue" galaxies with excessive UV-emission.
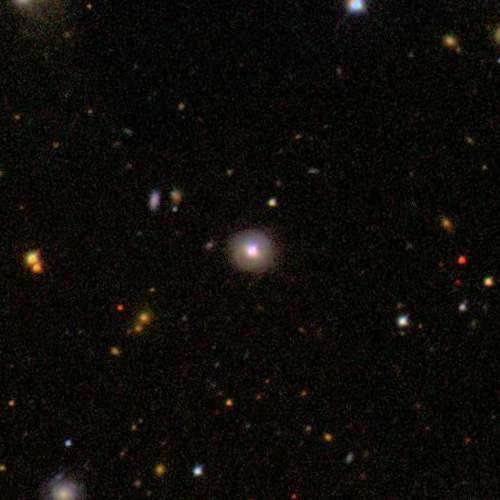
MRK 478 was detected as a very compact, star-like object. As a blue
star-like object it was also detected by both the
Palomar-Green Bright Quasar Survey (PG) and the Extreme Ultraviolet
Explorer (EUVE). The quasar host is a spiral galaxy with an apparent
diameter of
30"×20". The host itself shows clear signs of disturbance, detectible
as faint shells or arms. The very
bright nucleus emits a Narrow-Line Seyfert 1-spectrum (NLS1), very
similar to that found with I Zw 1. MRK 478 is a low amplitude variable object with a total range of less than 1 magnitude. Visual observers need at least an 8- to 10-inch telescope to glimpse this stellar object. Using large aperture telescopes, the quasar becomes either star-like or a star-like object, enveloped by a very diffuse and small halo. With very large aperture and high power, observers may recognize a slightly bluish hue of the bright star-like nucleus, a result of the UV-excess of this active galactic nucleus. CCD observers, as well as visual observers, shall use the comparison stars given above. ____________
Finding
MRK
478
is an easy task due to its position 3.5° SE of Gamma Bootis. A little
south of Gamma
Bootis, a
chain of
stars of mag 6 and mag 7 directly point to the quasar. Only 1.5° NE, we
find the faint galaxy NGC
5695, also known as MRK 686,
an active galaxy with S2-spectrum. As with MRK 478, this AGN was also
found by the UV-Continuum-Survey mentioned above.
Observers who like to track down some more very old quasi-stellar photons may turn to quasar PG 1411+442, a bright 14-mag object at a distance of about 1×109 light-years, some 10° NW of MRK 478. Another bright quasi-stellar object is PKS 1424+240, a variable 14-mag BL Lac object, located about 12° SSW of MRK 478. |
| de Grijp, M.H.K., Miley, G.K., et al. 1987, A&AS, 70, 95; Warm IRAS Sources. I. A Catalogue of AGN Candidates from the Point Source Catalogue (PSC). Gondhalekar, P.M., Kellett, B.J., et al. 1994, MNRAS, 268, 973; ROSAT/XRT-PSPC Observations and the Ionizing Continuum of the Seyfert 1 Galaxy Mrk 478. Hansen, T. 1991, Deep Sky Magazine 34, 32; The "Deepest" Deep Sky Objects. Karge, S.; Helle Quasare für 8- bis 10-Zoll Teleskope. Ein Beobachtungsführer zur visuellen Beobachtung von Quasaren und BL Lacertae Objekten; Frankfurt 2005. Khachikian, E.E., Weedman, D.W. 1974, ApJ, 192, 581; An Atlas of Seyfert Galaxies. Markarian, B.E., Lipovetzki, V.A. 1972, Astrophysics, 8, 89; Galaxies with Ultraviolet Continuum V. Peterson, B.M., Fricke, K., et al. 1981, PASP, 93, 281; UBV Photometry of Markarian and S0 galaxies. Schmidt, M., Green, R.F. 1983, ApJ, 269, 352; Quasar Evolution derived from the Palomar Bright Quasar Survey and other complete Quasar Surveys. Steinicke, W.; Katalog heller Quasare und BL Lacertae Objekte; Umkirch 1998. Steinicke, W.; Beobachtungsliste für helle Quasare; Umkirch 1999. Véron-Cetty, M.-P., Véron, P. 2001, A&A 374, 92; A Catalogue of Quasars and Active Nuclei: 10th edition. Véron-Cetty, M.-P., Véron, P. 2003, A&A 412, 399; A Catalogue of Quasars and Active Nuclei: 11th edition. Véron-Cetty, M.-P., Véron, P. 2006, A&A 455, 776; A Catalogue of Quasars and Active Nuclei: 12th edition. Véron-Cetty, M.-P., Véron, P. 2010, A&A 518, 10; A Catalogue of Quasars and Active Nuclei: 13th edition. Webb, W., Malkan, M. 2000, ApJS, 130, 165; Comparison star sequences for optical photometry of Active Galactic Nuclei and Quasars. |
| Links: APASS Chara/PEGA Sloan Digital Sky Survey |
| home |